ASSET – AI for Sustainable Prevention of Autoimmunity in the Society
Short description
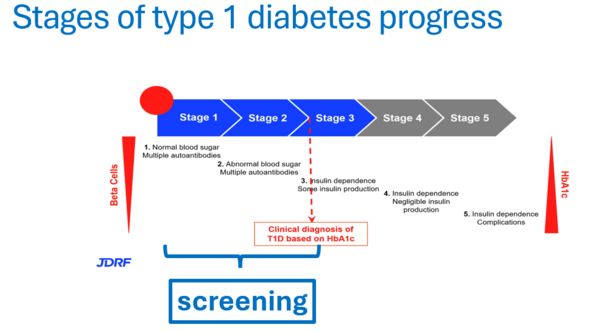
Early detection of type 1 diabetes is important. In stages 1 or 2 of the disease, specific diabetes antibodies are present, but blood sugar is usually close to normal. Early diagnosis can prevent or delay the onset of stage 3, i.e., manifest diabetes.
Using AI technology with existing large databases, this study aims to develop a screening method that assesses the risk of type 1 diabetes in children and young people.
Sweden has the world’s second-highest incidence of type 1 diabetes and national quality registries, providing unique opportunities to conduct research that can influence the development of diabetes.

Background
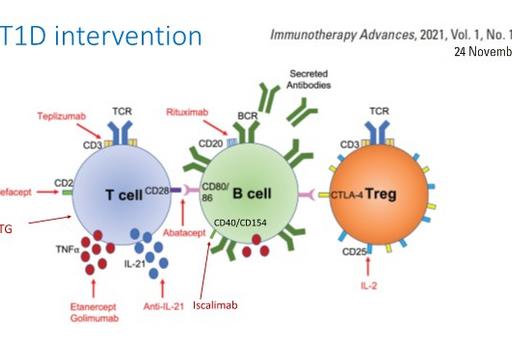
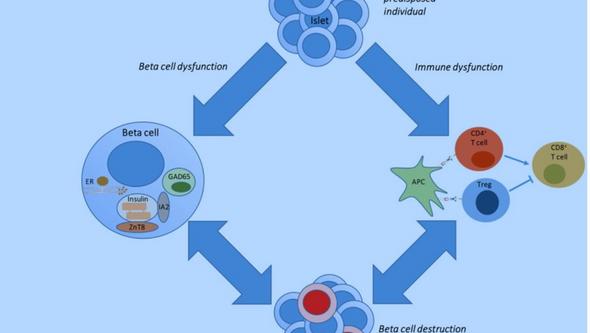
Type 1 Diabetes (T1D) is one of the most common chronic autoimmune diseases in children, arising when the body’s own immune system breaks down the pancreatic islet beta cells resulting in a lifelong dependence on exogenous insulin administration. T1D is a complex and heterogenous disease and there is a clear unmet need in terms of early risk detection and individualized preventative therapies.
ASSET (Artificial Intelligence [AI] for Sustainable Prevention of Autoimmunity in the Society) is a multidisciplinary consortium assembling commercial actors in the fields of autoimmune diseases and applied artificial intelligence, as well as academic and public healthcare institutions. Thegoal is to harness the wealth of data available from cohort studies and clinical trials to develop a prediction tool based on AI and machine learning to facilitate precision health and treatments starting with a Type 1 diabetes prevention pilot program. In parallel, ASSET will study the organizational and legal prerequisites to implement the proposed precision health solutions in the Swedish healthcare system.
Methods / Expected results
The project is divided into three main phases. 1) Development, where the technical basis for an AI tool is built and preparations for a pilot study are carried out; 2) Pilot, where prospective screening and prevention is evaluated 3) Scale-up, where tools are further developed and implementation and expansion to other indications is planned.
Analysis of available clinical data from long-term longitudinal cohort studies, such as of the more than 3 million data points retrieved from the TEDDY study, will be performed using a selection of machine learning / AI methodologies. Tools will be developed aiming at individualized prediction of risk for developing T1D and related co-morbidities. The tools will also be used to optimize screening programs to better identify subjects to be randomized in clinical trials, enabling more targeted and efficient clinical trials as well as optimizing variables and procedures for screening. Specifically, individuals will be identified who are likely to benefit from targeted prevention with specific investigational interventions.
The project will also aim to answer ethical, technical and organizational questions about how to carry out screening for Type 1 diabetes risk at a nation-wide level, including offering treatment based on individualized response predictions.
Conclusion
ASSET is funded by the Swedish Innovation Agency (VINNOVA) and constitutes one of the largest investments to assess screening and prevention for Type 1 diabetes ever made in the Nordic countries. This 5-year project aims to initiate an integrated approach to better disease prediction and targeted prevention, starting with T1D but with potential to expand into other indications. The project also aims to analyze current hurdles for the implementation of screening programs in a Scandinavian healthcare system.
Collaboration with other initiatives within prevention of autoimmune diseases at the Nordic and European level would allow the alignment towards a common strategy to achieve precision health.